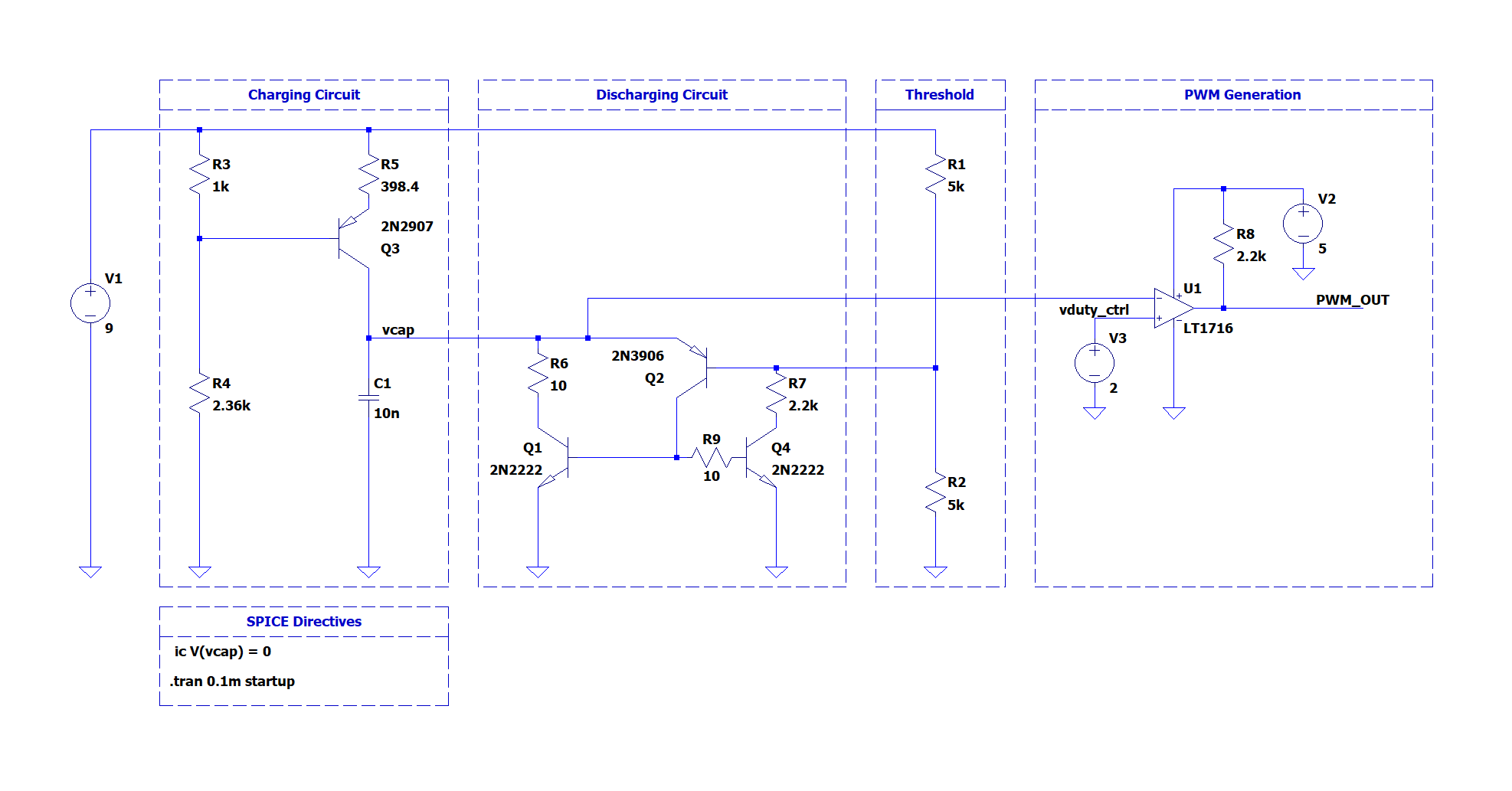
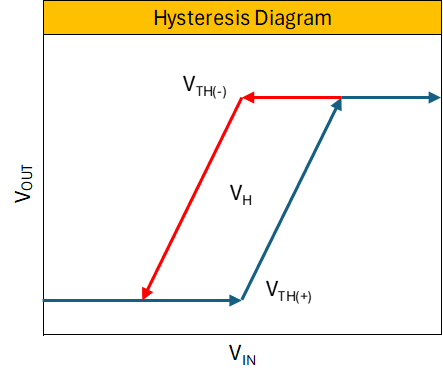
Analog Transistor Pulse Width Modulation Circuit
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a form of digital signal encoding where a unipolar, rectangular waveform's duty cycle is varied to control the average voltage delivered to a load. The signal is characterized by a fixed frequency and amplitude, with the effective average voltage determined by the ratio of the pulse width to the total time period. This ratio is often referred to as the "duty factor", or "duty cycle". In other words a 75% duty cycle (0.75) means the signal is on for 75% of the time period, and off for the remainder 25%. In this article the design...
[Read More]